foo = x^2 + sin(5*y) / exp(67*z);
The semicolon at the end is optional.
sin(x),cos(x),exp(x),log(x),atan(x),cosh(x),sinh(x),mean(x),median(x),etc.
x = [1,3,9,11,-10.2];
foo = x(3); % extracts third element in the array
x(2) = 27; % reassign element in the array
x = 1:15 % creates an array with the number 1 through 15
x = 4:2:28; % creates an array starting at 4 and going up by 2 until it gets to 28
x = -1.3:0.1:1.3; %creates an array starting at -1.3 and going up by 0.1 until it gets to 1.3
x = 1:2:6; % x = [1,3,5]
x = 0:0.1:10;
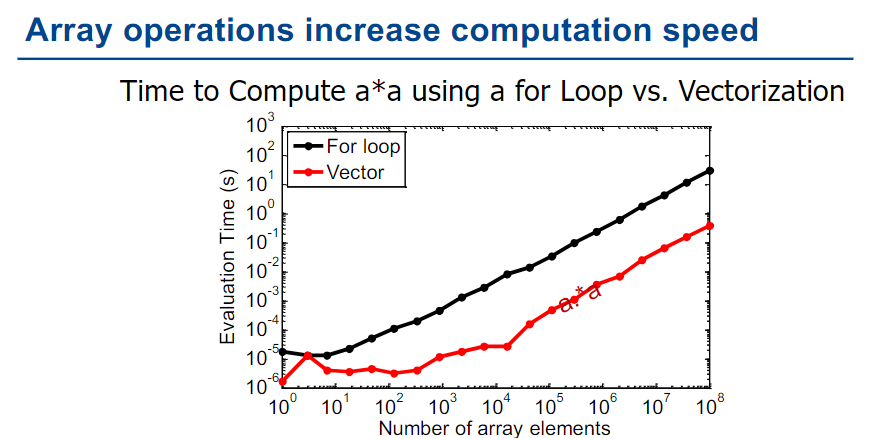
y = exp(5*x).*sin(x); % evaluate an expression on every element in the array x producing a new array called y
plot(x,y);
x = [1,2,3,4,5];
y = [7,8,9,10,11];
z = x + y; % element-wise addition adds corresponding elements
z = x.*y; % element-wise multiplication
z = x./y; % element-wise division
X = uint8(78); Y = uint8(190);
Z = X + Y;
% overflow - value will be clipped to 255
Note that numbers in scientific notation have the following components
When an array variable is created all of the numeric values in that array share the same numeric type. For example we can talk about an array of uint16s or an array of doubles.
x = single(0:0.1:100);make an array of single precision(单精度) numbers
whos
Lists all of the variables currently in your workspace and shows you their typesclear
Clears all of the variables in your workspace – you can also use this to clear specific variablesclc
Just clears the command window – has no effect on the workspacefunction f = fact(n)
f = prod(1:n);
end
function [output1,output2,output3] = myFunction(input1,input2,input3)
Must start with a letter from the alphabet
function out1 = testFunction(in1)
% A test function
% this would report, in the help function, all of functionality of the function
% in1 = function input (units: not specified)
% out2 = function output (units : not specified)
(in the command window)
lookfor 'a test function'
% testFunction - A test function
help testFunction
% A test
% this would report, in the help function, all of functionality of the function
% in1 = function input (units: not specified)
% out2 = function output (units : not specified)
userpath('C:\ATRI')
addpath() functionrmpath() functionfunction_name = @ (arguments) expression
FtoC = @ (F) 5*(F-32)./9
% examples
FA = @ (x) exp(x^2)/sqrt(x^2+5)
FA(2)
FA = @ (x) exp(x.^2)./sqrt(x.^2+5)
FA([1 0.5 2])
f = @sin;
m = fminbnd(f,0,2*pi)
q = integral(@cubicPoly,0,1);
% Linspace and logspace
x = linspace(1,5,5)
x = logspace(1,5,5)
x = [5, 9, 4, 1, 7, 3, 4, 8]
% Accessing vector elements
y = x(1)
y = x(1:3)
y = x(end)
y = x(end-2)
y = x([1,3,6]) % y = [5,4,3]
% The indices start at 1, not 0.
% Overwriting
x(end) = 1;
%Add ending indices
x(end+1) = 8
x(end+1:end+2) = [6,9]
%Removing elements
x(1) = []; % Remove the first element
x(end-3,end) = [];
for jj = 1:20
disp(jj)
end
a = 1;
while a < 10
a = a + 1;
end

if statementa = 1;
b = 2;
if a == 1;
disp('a is equal to 1! Yeah');
end
elseif a == 1 && b == 2;
disp('...')
end
| Logical Operator(Scalars) | Logical Operator(Vectors) | Function Call |
|---|---|---|
| && | & | and(a,b) |
| || | | | or(a,b) |
| ~ | ~ | not(a) |
| none | none | xor(a,b) |
Attention: ~= in matlab equals to != in other languages |
a = [1 6 5] < 2
% a = [1,0,0]
x = [5 9 2 4 3];
v = logical([1 0 1 0 1]);
xp = x(v);
% xp = [5,2,3]